
Published on: Jan 8, 2025
Revolutionising Supply Chains with Agentic AI.
I. Introduction
Modern supply chains are becoming increasingly complex and volatile, facing challenges from global disruptions, fluctuating demand, and the need for real-time visibility. Traditional methods, such as manual tracking and outdated systems, are no longer sufficient to handle these complexities. Agentic AI offers a promising solution by automating and optimising complex processes, and autonomously completing tasks efficiently.
II. Challenges in Modern Supply Chain Management
- Market Volatility and Disruptions: Unpredictable global events, natural disasters, pandemics, and geopolitical tensions cause significant delays and inefficiencies in supply chains. These disruptions make it difficult to maintain consistent operations and meet customer demands.
- Demand Fluctuations: Managing fluctuating customer demand requires real-time data analysis and agile responses to avoid stockouts or overstocking. Inaccurate demand forecasts can lead to both lost sales and excess inventory.
- Inefficiencies of Traditional Systems: Manual tracking, outdated inventory systems, and siloed data hinder efficient operations. These systems often rely on past data and result in inaccurate forecasts, as well as slow response times.
- Lost Sales: Delays in answering critical supply chain questions can result in a significant percentage of lost sales.
- Data Overload: Procurement functions are often overwhelmed with data that is not used effectively to improve decision-making. This can lead to missed opportunities for cost savings and efficiency improvements.
- Integration Issues: Integrating advanced AI solutions with existing rule-based legacy systems presents a challenge. Seamless integration is crucial for leveraging AI without disrupting established workflows.
III. Introduction to Agentic AI
Agentic AI uses AI agents to complete complicated and effort-intensive processes. These agents can break down assigned work into smaller parts and function autonomously to complete tasks in a highly efficient manner. They can perceive, reason, act, and learn without constant human guidance, which makes them ideal for handling complex tasks and streamline automation efforts and ensure efficient progress.
Unlike traditional AI or GenAI, which may require specific data and cannot act independently, Agentic AI is capable of autonomous decision-making and action. Agentic AI is capable of handling repetitive, data-intensive processes. Vanilla LLMs may lack the contextual knowledge of custom data to answer complex queries, which is where Agentic AI excels.
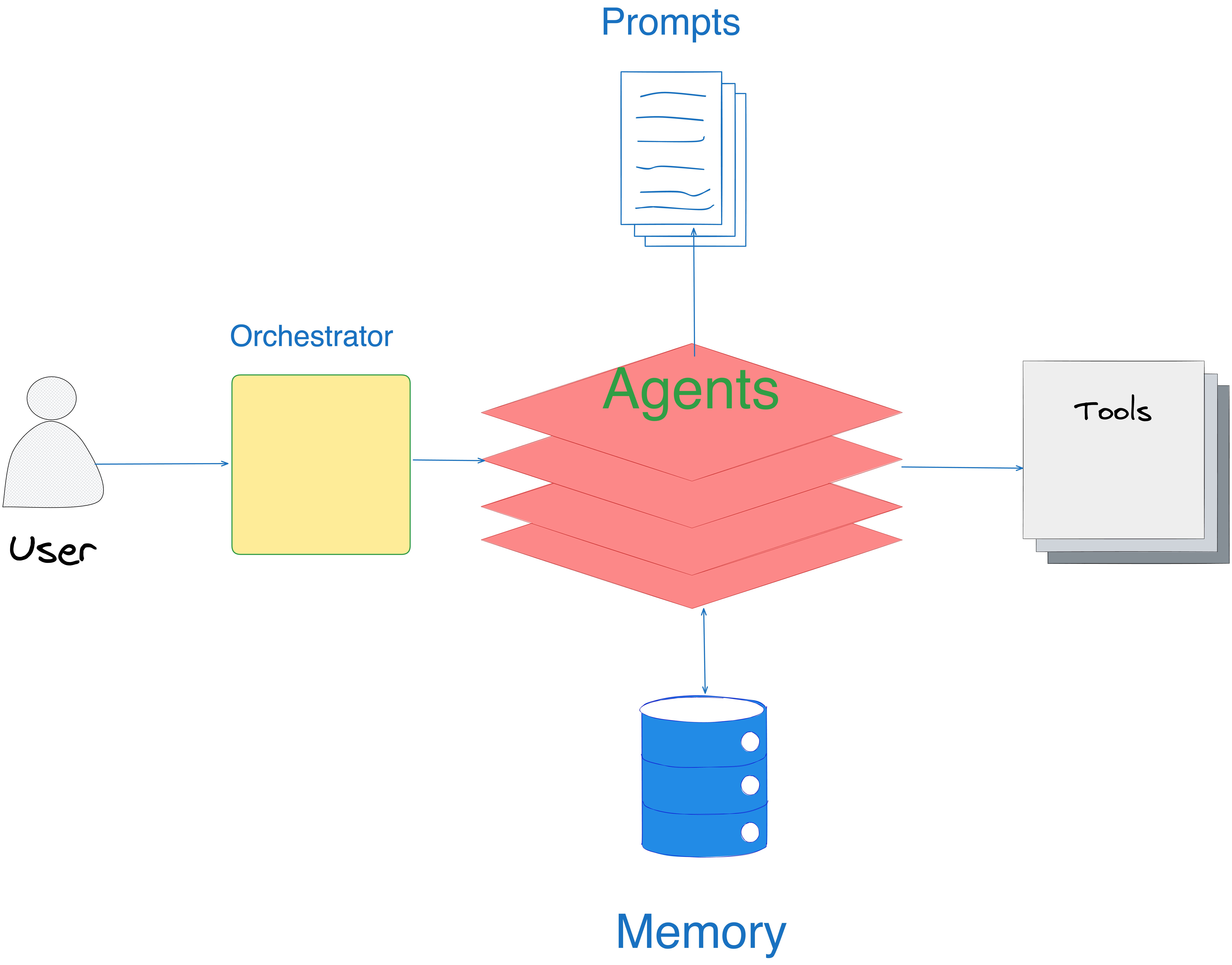
Core Components of AI Agents:
AI agents consist of Large Language Models (LLMs) for processing, memory to store and retrieve information, tools to perform actions, and knowledge to inform decision-making (planning).
- Memory includes short-term memory for adhering to a plan and long-term memory for downstream processes to use upstream results. Short-term memory allows agents to access outputs within the context of a workflow, while long-term memory allows access to previously executed outputs.
- Tools are executable functions or sub-flows that complete intermediate tasks. For example, tools can be used to fetch changelogs, read repository files, or interact with databases.
- Knowledge is the data that agents use to perform tasks. This could be data extracted from sources like Logs, customer databases, or market reports, etc.
Types of AI Agents:
- Simple Reflex Agents make decisions based only on current observations, ignoring past inputs.
- Hierarchical Agents use a layered tree structure where higher-level agents direct lower-level ones, which helps manage complexity. For example, a Product Manager agent can delegate tasks to a Developer agent. However, uni-directional communication between agents is more effective for automation than bi-directional communication in a hierarchical structure.
- Multi-Agent Systems involve groups of agents that collaborate to solve complex problems.
- Custom-Agent Systems involve groups of agents that collaborate to solve complex problems and are stitched together based on custom domain specific workflow.
IV. How Agentic AI Can Solve Supply Chain Challenges
- Enhanced Data Analysis and Decision-Making: AI agents can process vast amounts of data from various sources and make informed decisions in real-time. They use advanced analytics and machine learning to identify inefficiencies, forecast demand, and optimise processes.
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Agentic AI can automate tasks such as data entry, compliance checks, and transaction processing, freeing employees for more strategic work. It can also automate workflows, reducing human intervention to minimise errors and accelerate processes.
- Improved Efficiency and Cost Reduction: AI agents can optimise inventory levels, predict demand, and improve routing. This leads to reduced costs, improved efficiency, and minimised waste.
- Inventory Management: AI can analyse historical and real-time data to predict demand accurately, optimising stock levels and reducing both stockouts and overstocking. This helps to reduce warehousing costs.
- Route Optimisation: AI can dynamically allocate resources, predict the most fuel-efficient routes and reduce unnecessary fuel consumption and labour costs.
- Proactive Problem Solving: AI agents can predict potential delivery issues and communicate them proactively, ensuring timely resolutions. This allows businesses to adapt quickly to fluctuating demand and supply chain disruptions.
- Real-Time Visibility: AI agents provide real-time tracking of shipments, enhancing transparency and customer confidence. Logistics managers can identify delays or inefficiencies by visualising shipment performance across regions.
- Improved Vendor and Supplier Management: AI can manage supplier relationships, evaluate performance, and efficiently source raw materials, which reduces time instabilities and communication issues.
- Enhanced Customer Service: AI agents can handle customer inquiries about order status, delivery fees, and delivery times, providing real-time communication and improving overall satisfaction. They can also provide 24/7 support through AI chatbots.
V. Practical Applications of Agentic AI in Supply Chain
- Supply Chain Optimisation: AI agents analyse and control supply chain mechanisms, predict demand, and improve inventory management. They can parse through extensive log and metadata files and advise supply chain planners and leaders in building risk-resilient networks.
- Automated Warehouses: AI-powered robots can enhance efficiency in sorting, picking, and packing processes, ensuring efficient order delivery.
- Logistics Optimisation: AI agents optimise inventory management, demand forecasting, and route planning. They can also recommend the most efficient delivery routes and optimal vehicle load distribution.
- Recruitment Automation: AI agents can search vast databases of resumes and social media profiles to find candidates, extract relevant information, and schedule interviews, streamlining the hiring process.
- Customer Service Automation: AI can be trained on customer interactions, browsing history, and preferences to answer queries effectively, providing 24/7 support through chatbots and personalised recommendations.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: AI can analyze customer behaviour to offer tailored product suggestions and instant promotions, enhancing the shopping experience and driving sales.
- Process Optimisation: AI agents can identify areas of inefficiency in supply chain operations, and suggest improvements to reduce costs, speed up processes, and enhance overall performance.
VI. Implementation Considerations
- Organisational Readiness: It is important to assess the existing technology, budget, and expertise before implementing AI. Suppliers should audit their existing supply chain structures to understand where AI can be implemented.
- Identifying Suitable Processes: Choose processes that are repetitive, error-prone, data-intensive, or require complex decision-making.
- Technology and Infrastructure Requirements: Deploying AI agents requires a robust data processing infrastructure, sufficient computational power, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Data Quality: Ensuring high-quality data collection that reflects customer behaviour and operational performance is crucial for effective AI implementation. Data should be collected through the right techniques.
- Ethical Considerations: It is important to address potential biases in data, ensure security of sensitive information, and maintain transparency in AI operations.
- Integration of Agentic AI: Seamless integration with existing systems used in a supply-chain is crucial for a smooth transition. Solutions should allow for a "do-it-yourself approach" for creating novel use cases.
VII. Future Trends
- Increased Interconnection with IoT: AI agents will interpret real-time data from IoT devices and make preventative decisions, further enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
- Hyper-Personalisation: Logistics will be customised to meet individual customer needs, enhancing satisfaction and loyalty. This includes tailored, delivery preferences, product recommendations and promotions, etc.
- Sustainability Initiatives: AI will play a key role in optimising supply chains to increase environmental sustainability. AI helps businesses deliver goods faster and cut expenses at the same time, therefore making shipment eco-friendly, reduce wastage in F&B sector.
- Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration: AI agents and humans will work together, leveraging the strengths of both. This will enable teams to tap into the abilities of both human and artificial intelligence.
- Responsible AI Practices: Accountable and transparent AI practices are needed to ensure ethical use of data. More responsible AI is needed because of the increasing application of AI in firms.
VIII. Conclusion
Agentic AI has the potential to revolutionise the logistics and supply chain management sectors. Adopting AI-driven solutions is essential for future success, enabling a shift to proactive rather than reactive supply chains. Competition in the business will mostly be determined by the acceptance and incorporation of AI agents.
IX. Sector Specific Use Cases
-
Supply Chain:
- Intelligent Query Handling: AI agents can parse through extensive log and metadata files, like SAP IBP Optimizer Logs, to answer complex supply chain questions. This is something LLMs cannot do on their own.
- Risk Management: AI can be used to build risk-resilient networks by analysing potential disruptions and suggesting mitigation strategies.
- Data Driven Decision Making: AI helps convert data into actionable insights for strategic planning and operational activities. Advanced analytics provide insights into supply chain efficiency.
- Automated Document Processing: AI agents can quickly pull relevant information from documents like supplier ESG reports, contracts, and filings, saving time and improving efficiency. This allows personnel to focus on more innovative projects.
- Process Optimization: AI can analyze historical data to identify areas for improvement, such as bottlenecks or inefficient routes.
-
Retail:
- Personalised Marketing: AI agents analyse customer data, including demographics, purchase history, and preferences to segment customers and deliver tailored recommendations.
- Real-Time Tracking: Customers can track their orders in real-time to eliminate worry about delivery time.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI can execute dynamic pricing strategies using real-time market analysis, maximising revenue.
- Inventory Optimisation: AI helps predict demand and optimise stock levels, reducing stockouts or overstocking.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: AI can analyze customer purchase history and behavior to recommend related items and upgrades, increasing sales opportunities.
-
FMCG (Fast-Moving Consumer Goods):
- Demand Forecasting: AI agents improve demand forecasting to ensure sufficient supply, reducing the potential for lost sales.
- Procurement Optimisation: AI can analyse supplier performance, manage tenders, and source raw materials at the right price and time.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI can analyse customer behaviour to offer tailored product suggestions and promotions.
- Process Optimization: AI can streamline surrounding business processes, such as order processing and inventory management.
-
F&B (Food and Beverage):
- Inventory Management: AI enables precise inventory management to minimise waste, which is especially critical in the food and beverage sector due to perishability.
- Quality Control: AI agents can monitor the quality of raw materials and finished products, ensuring compliance with standards.
- Route Optimisation: AI helps optimise delivery routes to maintain the freshness of perishable goods and reduce transportation costs.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: AI can suggest complementary items based on customer orders and preferences.
- Process Optimization: AI can be used to manage supplier relationships and evaluate their performance to ensure that raw materials are sourced at the right price and time.