Published on: Apr 11, 2025
On-Demand Image Resizing with Google Cloud: A Cost-Efficient CDN Approach
Introduction
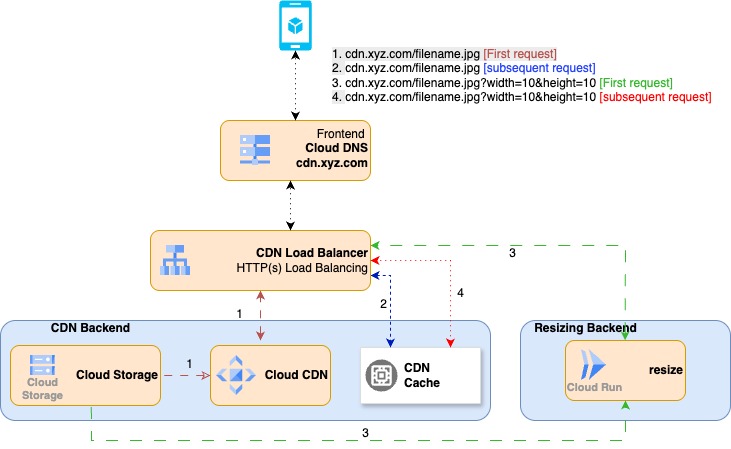
We needed to serve images to our frontend application. These images were in a GCS bucket. In addition, we needed to serve images of various resolutions and we didn't want to store all image sizes in the bucket. We chose to use a combo of CDN and load balancer on GCP to serve these images to the frontend. However, instead of storing all the variants of an image, we chose to generate resized versions on the fly when the frontend requests them--and cache those for performance and cost reasons.
Requirements:
- Dynamically resizes images on demand
- Caches generated sizes efficiently, to reduce compute costs
- Integrates seamlessly with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services
Architecture Overview
Our final solution combined four key GCP services:
- Google Cloud CDN: Caches resized images at edge locations
- Global Load Balancer (GLB): Routes requests based on query parameters, between CDN and Cloud Run resizing services
- Cloud Run: Stateless container for image processing
- GCS Bucket: Stores original high-resolution images
Implementation Walkthrough
General steps to follow for the implementation
- Deploy a resizing service (Cloud Function/Cloud Run) that takes parameters (e.g., image path, width, height) and returns the resized image.
- Configure the Load Balancer's backend service to point to this resizing service, and enable Cloud CDN on it.
- Set up the route rules for URL Map structure so that requests for resized images include the parameters, like width and height.
- The resizing service fetches the original image from GCS, resizes it, and returns it with appropriate Cache-Control headers so Cloud CDN caches it.
- The CDN then serves subsequent requests for the same size from the cache.
1. Dynamic Resizing Service (Cloud Run)
We chose Cloud Run over Cloud Functions for better control over containerization and longer request timeouts. The service uses Express.js and Sharp - a high-performance Node.js image processing library.
Key features of the resizer:
1const express = require('express');
2const sharp = require('sharp');
3const { Storage } = require('@google-cloud/storage');
4const storage = new Storage();
5const app = express();
6app.get('/:filename', async (req, res) => {
7 const { filename } = req.params;
8 const width = parseInt(req.query.width) || undefined;
9 const height = parseInt(req.query.height) || undefined;
10 try {
11 const bucket = storage.bucket('sb-listing-data');
12 const file = bucket.file(filename);
13 const [exists] = await file.exists();
14 if (!exists) return res.status(404).send('Not found');
15
16 const readStream = file.createReadStream();
17 let pipeline = sharp();
18 if (width > 2048 || height > 2048) {
19 return res.status(400).send('Maximum size 2048px');
20 }
21 if (width && height) {
22 pipeline = pipeline.resize(width, height, { fit: 'inside' });
23 }
24 res.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=2629800'); // Cache for 1 month
25 res.setHeader("content-type", "image/jpeg");
26 readStream.pipe(pipeline).pipe(res);
27 } catch (error) {
28 res.status(500).send('Error processing image');
29 }
30});
31exports.resizer=app;Critical caching headers ensure proper CDN behavior:
1res.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=2629800'); // 1 month
2res.set('Content-Type', 'image/jpeg');
3res.set('Vary', 'Accept, Width, Height'); // Prevent parameter collisions2. Intelligent Routing with Global Load Balancer
The GLB's URL Map routes requests based on query parameters:
1defaultService: projects/xyz/global/backendBuckets/cdn-fe
2name: url-map-query-params
3routeRules:
4- matchRules:
5 - queryParameterMatches:
6 - name: width
7 presentMatch: true
8 - name: height
9 presentMatch: true
10 pathTemplateMatch: /{filename=*}
11 priority: 1
12 service: projects//global/backendServices/resizerRouting Logic:
| Request Type | Example URL | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| With width & height params | /images/cat.jpg?width=300&height=200 | Cloud Run Resizer |
| All other requests | /images/cat.jpg | GCS Bucket |
Some other considerations
- The resizing service should handle errors, like invalid sizes or missing images. Also, using a CDN requires setting proper cache headers. The service should return Cache-Control: public, max-age=... so the CDN caches it.
- Security: Ensure that the service can't be abused to generate too many sizes, possibly adding rate limiting or size restrictions.
- Cost: Processing images on demand with Cloud Run/Cloud Functions incur costs based on the number of requests and processing time. Caching with CDN reduces the number of times the backend is hit and avoids saving different images sizes.
- Cache Invalidation: Implement versioned URLs (/v2/images/...) to force CDN refresh when updating resizing logic.
- Error Handling: Custom error pages prevent CDN caching of error states:
javascript
1.on('error', (err) => { 2 res.status(500).sendFile('error500.jpg'); 3}); - Monitoring: Critical Cloud Monitoring metrics:
- CDN Cache Hit Ratio
- Resizer 5xx Errors
- Backend Latency Percentiles
- Alternative Image Protocols, this example is limited to jpeg.
- WebP/AVIF format support
- Density-aware srcset generation
- Auto-Cropping/watermark-removal/blurring etc, consider other applications using Cloud Vision API
Conclusion
This architecture reduced our image storage costs by 70% while maintaining sub-200ms response times for cached assets.